Set up Falcon TTS Server
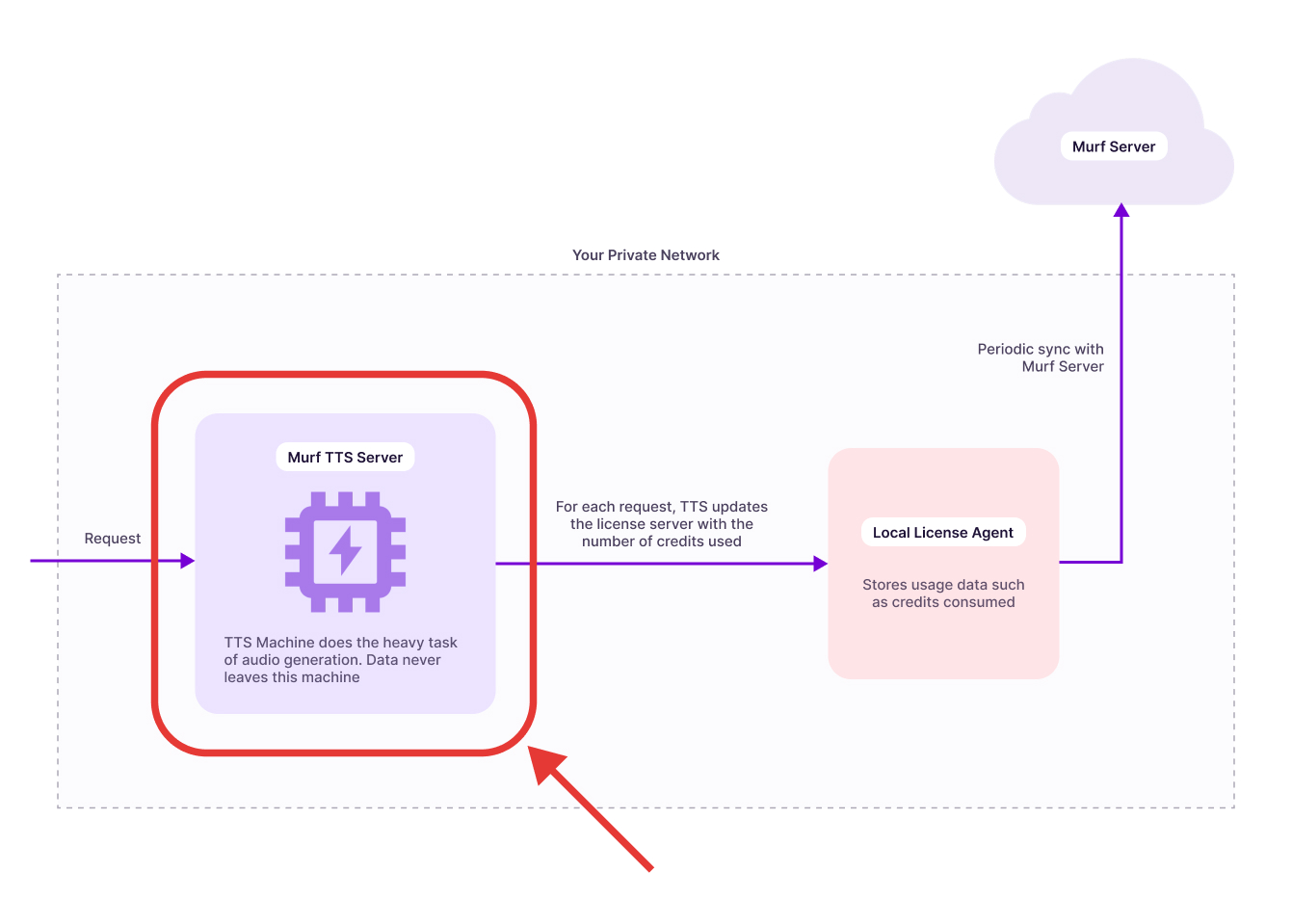
The Falcon TTS Server is the core engine of Murf’s on-prem text-to-speech system. It processes text input and generates speech locally, delivering fast, high-quality output without relying on external APIs. Running Falcon within your own infrastructure ensures low-latency performance, data privacy, and full operational control.
Trial Deployment
This guide provides step-by-step instructions for deploying the Murf TTS (Text-to-Speech) service on an AWS EC2 instance using Docker with GPU acceleration.
Prerequisites
Hardware Requirements
Minimum Requirements
Recommended Requirements
Software Requirements
Operating System
- Ubuntu 22.04 LTS (recommended)
- Amazon Linux 2023 (supported)
Required Software
- Docker Engine (20.10.0 or later)
- NVIDIA Container Toolkit (nvidia-docker2)
- NVIDIA GPU Drivers (version 525.60.13 or later)
- AWS CLI (configured with appropriate IAM permissions)
Pre-deployment Checklist
NVIDIA GPU Drivers Installation
Check if drivers are already installed:
If you see GPU information displayed, drivers are already installed and you can skip to step 3.
If drivers are NOT installed, install them:
Option A: Using Ubuntu Repository (Recommended for Ubuntu 22.04)
After reboot, verify installation:
Option B: Using NVIDIA Official Repository
Run nvidia-smi to verify the installation.
AWS GPU instances launched with Deep Learning AMIs or GPU-optimized AMIs usually have drivers pre-installed.
Docker Installation
Install Docker if not already installed:
Nvidia Container Toolkit Installation
Verify GPU Access
Test that Docker can access the GPU:
You should see your GPU listed with driver information.
Get the Docker Image
Murf team will provide you with the Docker image for the Falcon TTS Server. You will be provided with a docker pull command to pull the image.
Deployment Steps
Set Environment Variables
Create environment variables for your deployment:
Important: Replace your-secure-secret-key-here with your actual production secret key.
Run the Docker Container
Run the Docker container with GPU support:
Command breakdown:
-d: Run in detached mode (background)--gpus all: Enable access to all available GPUs-e TTS_MASTER_SECRET: Pass the master secret for authentication-e LLA_ENDPOINT: (Optional) Specify custom LLA server endpoint--name murf-tts: Name the container “murf-tts”-p 80:8000: Map host port 80 to container port 8000--restart unless-stopped: Automatically restart container unless manually stoppedLast parameter: Docker image URI
Verification
Check the Container Logs
Monitor the startup logs to ensure the service initializes correctly:
This should show the startup logs and the service should be ready to use.
Test the TTS Service
Option 1: Health Check via Browser Open your browser and navigate to:
You should see:
Option 2: Interactive Audio Test Page Navigate to the test page:
This provides a web interface to:
- Paste JSON payloads
- Generate speech
- Play audio directly in the browser
- Download WAV files
Option 3: API Documentation
View the interactive API documentation:
This opens the FastAPI Swagger UI for exploring all available endpoints.